Economy's Factors of Production
Land
- resources that are God-given from nature
Labor
- work done by human beings
Capital
Physical capital: consists of manufactured productive resources like equipment, buildings or tools
Human capital: skills and knowledge a worker gets from education
Entrepreneurship
- often referred to as the "4th Factor of Production," they combine the three resources to make innovative profits by taking risk
Derived Demand
Definition
- demand from a factor is dericed fomr firm's output.
Examples
If the demand for flight increase, then the demand for airline pilots will also increase
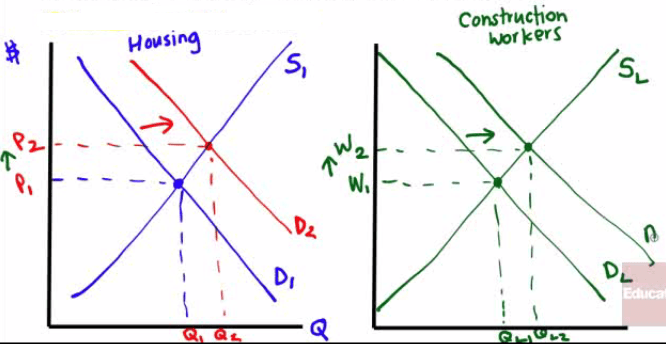
After Hurricane Katrina, the demand for houses increased, thus increasing the demand for construction workers.
Graph
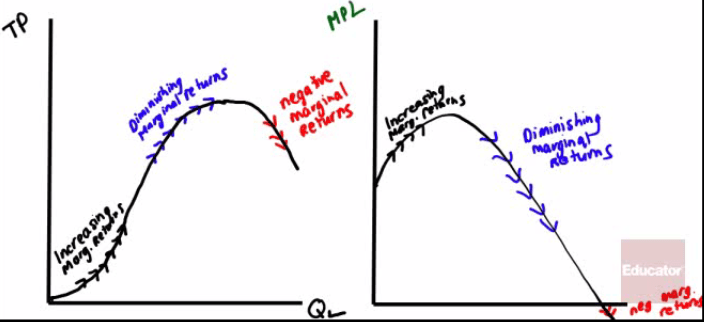
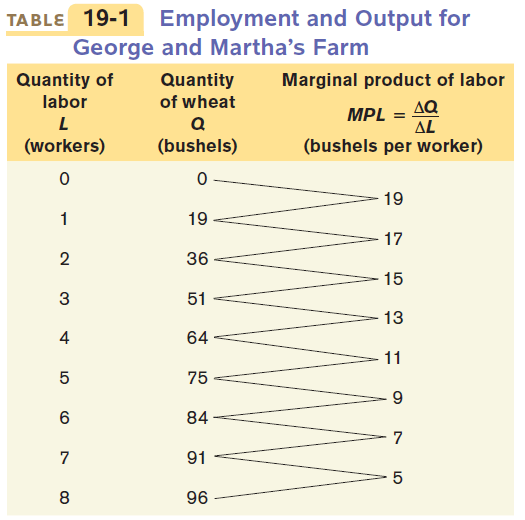
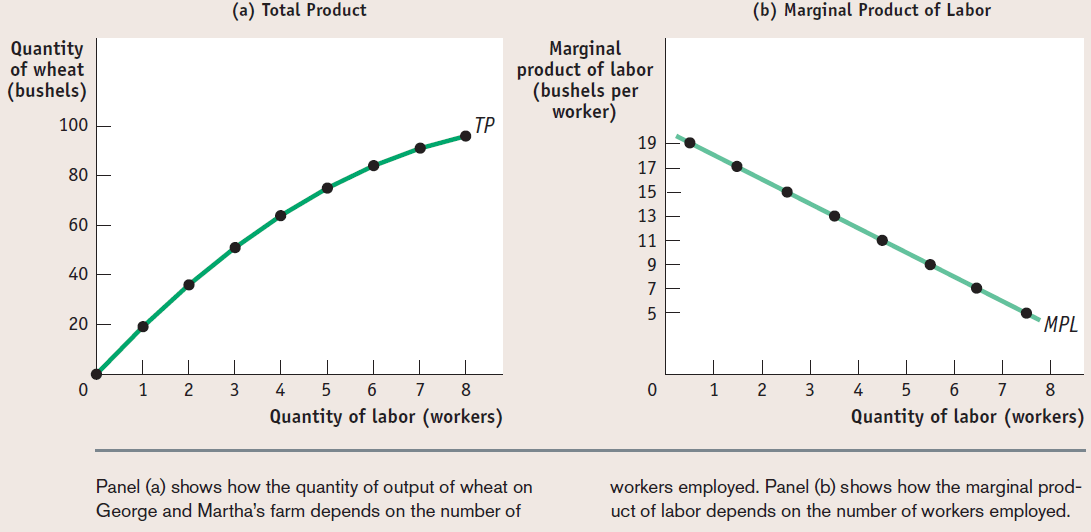
Total Product vs. Marginal Product
Total product shows the total quantity of output produced, which will eventually increase at a decreasing rate
Marginal product of labor will decrease as you hire more workers due to diminishing marginal returns
Value of the Marginal Product
Meaning
- The value of the marginal product of a factor is the value of the additional output generated by employing one more unit of that factor.
VMPL = Value of the Marginal Product of Labor
MRP = Marginal Revenue Product
Formula
VMPL = P * MPL
MRP = P * MPL
Hiring decision rule
Hire the extra worker if VMPL >W
VMPL = W at the profit-maximizing level of employment
Example
If the 5th worker produces 7 radios in the one day which sell for $10 each and his daily wage rate equals $10, should you hire the worker?
VMPL = P * MPL = 10 * 7 = 70 < W = 100
Curve
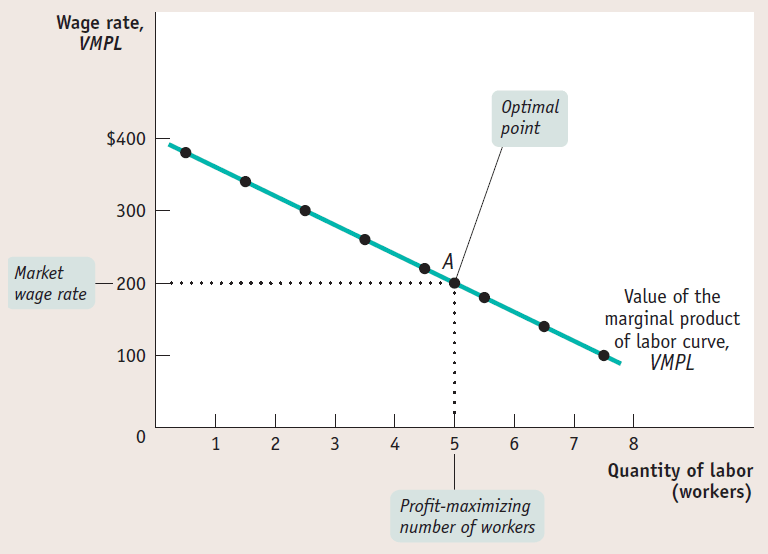
This curve shows how the value of marginal product of labor depends on the number of workers employed.
It slopes downward because of diminishing returns to labor in production
To maximize profit, you should choose the level of employment at which the value of the marginal product of labor is equal to the market wage rate
Shifts of the Factor Demand Curve
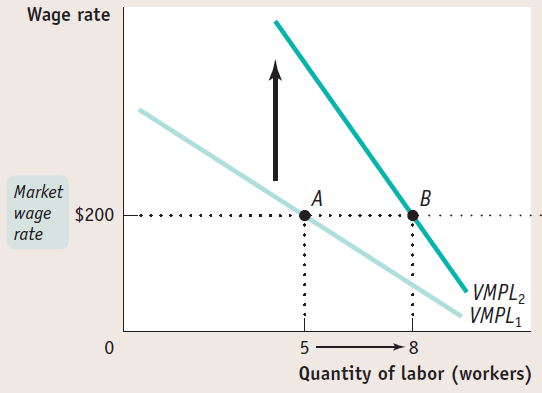
Changes in the price of goods
- If the price of wheat, increases, what happens to the VMPL of wheat?
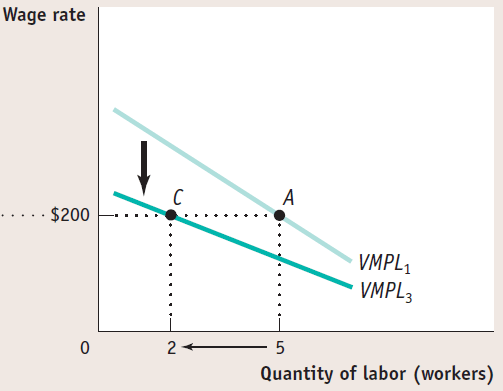
Change in supply of other factors
- If the workers decrease their productivity due to a loos of land, what happens to the VMPL?
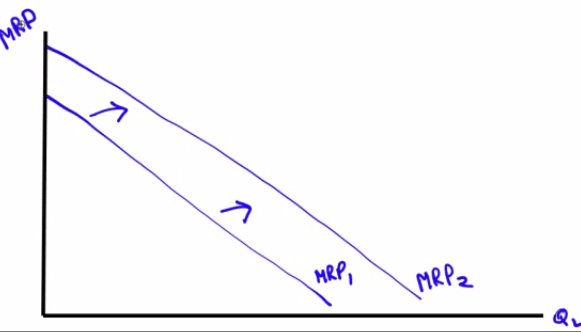
Changes in Technology
- The usual impact of technological process will shift the MPL (and thus VMPL) to the right
Factor Market Example
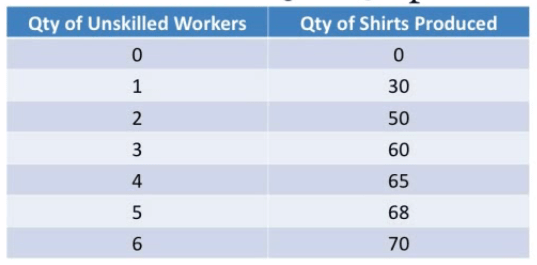
Assume that Samantha's Shirt Company sells shirts at $15 and pays a wage of $85 a day. Assume labor is the only output.
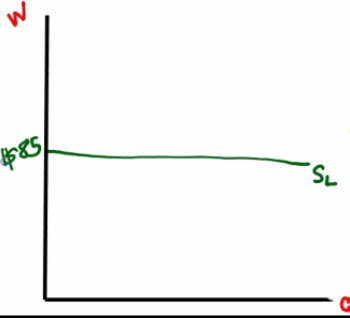
Draw a correctly labeled graph of SSC's current supply curve for unskilled labor
Put QL on the x-axis, and W on the y-axis
Perfectively competitive labor market
What is SSC's profit maximizing level?
| QL | Q | MPL | P | MRP/VMPL | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | ||||
| 1 | 30 | 30 | 15 | 450 | 85 |
| 2 | 50 | 20 | 15 | 300 | 85 |
| 3 | 60 | 10 | 15 | 150 | 85 |
| 4 | 65 | 5 | 15 | 75 | 85 |
| 5 | 68 | 3 | 15 | 45 | 85 |
| 6 | 70 | 2 | 15 | 30 | 85 |
When QL = 3, MRP/VMPL > W
When QL = 4, MRP/VMPL < W
Answer: Produce 60 shirts and hire 3 workers
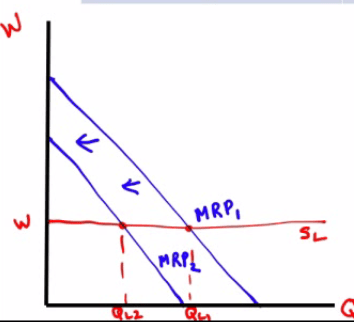
Suppose SSC loses technology that decrease the productivity of its unskilled workers. How will the new technology affect the quantity of unskilled labor SSC hires?
The MRP decreases, because MPL has decreased.
The quantity of Labor will decrease
How will the new technology affect the wage paid to SSC's unskilled workers
- Wage is unaffected because wage is perfectly elastic or constant
Another Factor Market Example
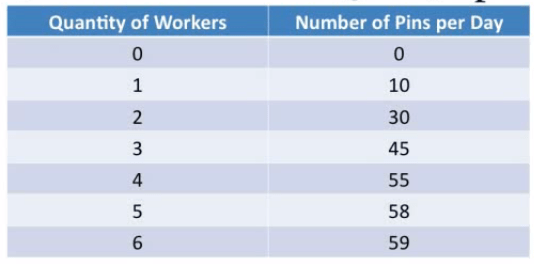
Sus & Jib is a profit-maximizing pin-making firm that can sell pins at a price of $20 each. Sus & Jib can hire workers at a market wage of $120 per day per worker
In what market structure does this company sell its products?
- perfect competition because price is the same and no differentiation.
In what market structure do the laborers work in?
- perfect competition because wage rate is constant
Calculate the value of the marginal product of labor of the third worker
- MRP = (45 - 30) * 30 = 15 * 20 = 300
What is the profit-maximizing output level?
| QL | Q | MPL | P | MRP/VMPL | W |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | ||||
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 200 | 120 |
| 2 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 400 | 120 |
| 3 | 45 | 15 | 20 | 300 | 120 |
| 4 | 55 | 10 | 20 | 200 | 120 |
| 5 | 58 | 3 | 20 | 60 | 120 |
| 6 | 59 | 1 | 20 | 30 | 120 |
- Profit-maximizing output level is 55-58 pins with 4-5 workers